What are the signs and symptoms of Celiac Disease?
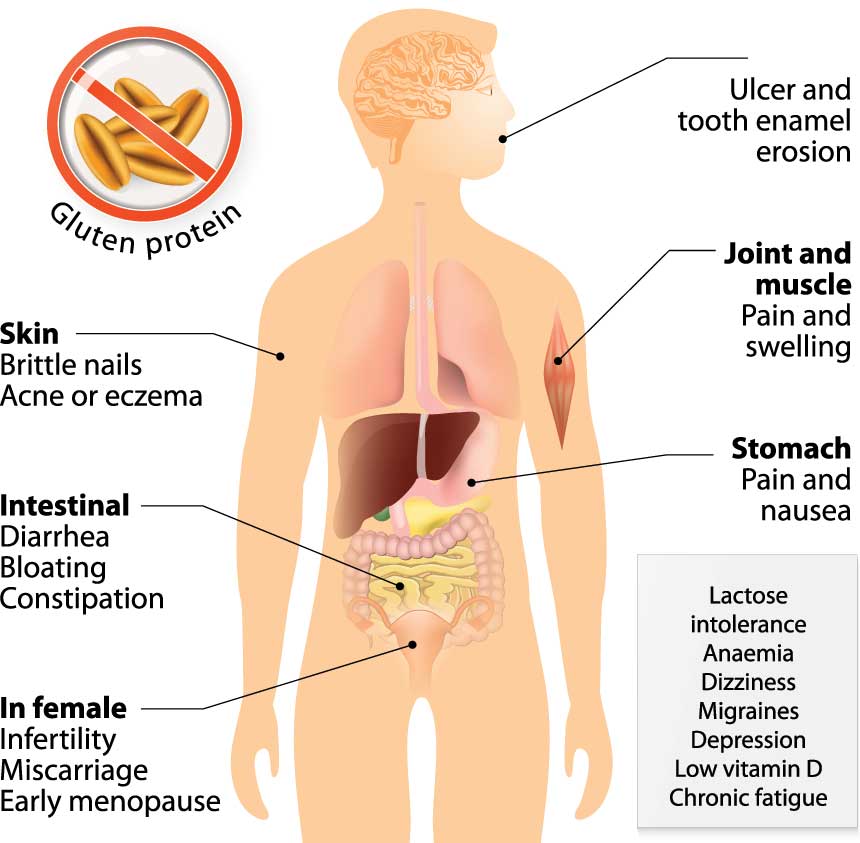
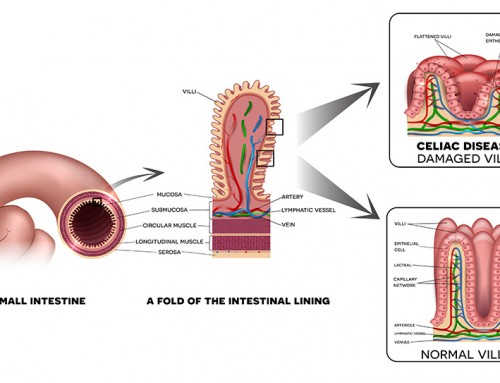
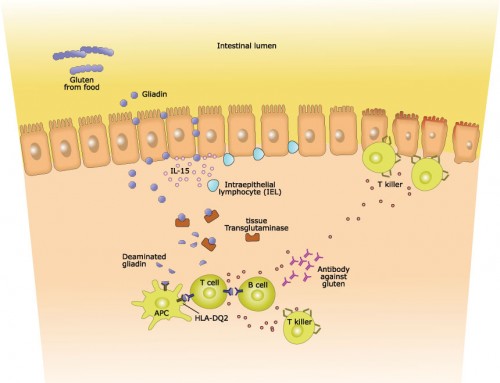
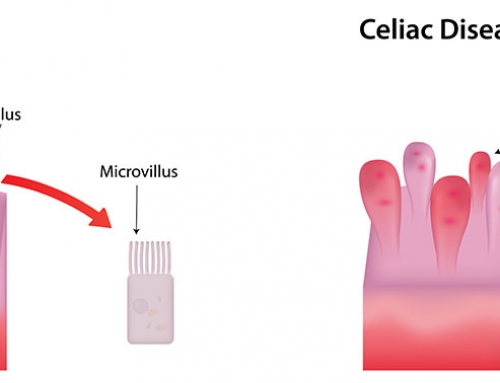
Classic celiac disease is associated with gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, weight loss, appetite changes, anorexia, lactose intolerance, abdominal distension and stools that float, appear fatty and smell foul. If the condition is left untreated, some people with celiac disease can develop other non-gastrointestinal symptoms over time due to malabsorption of essential vitamins and nutrients. These other symptoms include depression, epilepsy, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), migraines, anemia (low blood count), osteoporosis, dermatitis herpetiformis (itchy skin), vitamin deficiency, mouth ulcers, dental enamel defects, chronic fatigue, hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), numbness and tingling in the limbs, infertility or repeated miscarriages.
People suffering from non-classic celiac disease do not experience the typical gastrointestinal symptoms, but they still have intestinal damage and the non-gastrointestinal symptoms.
Children with celiac disease may experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, nausea and vomiting. They also tend to have growth defects, short stature and delayed puberty.
References:
Love K (Jan 2015). 10 Symptoms of Celiac Disease. Health Information, RMHealthy.com.
Rubio-Tapia A, Ludvigsson JF, Brantner TL, Murray JA, Everhart JE (2012). The prevalence of celiac disease in the United States. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 107(10): 1538-44.
DNA In the News2017-04-06T19:04:52+00:00