What is refractory Celiac Disease?
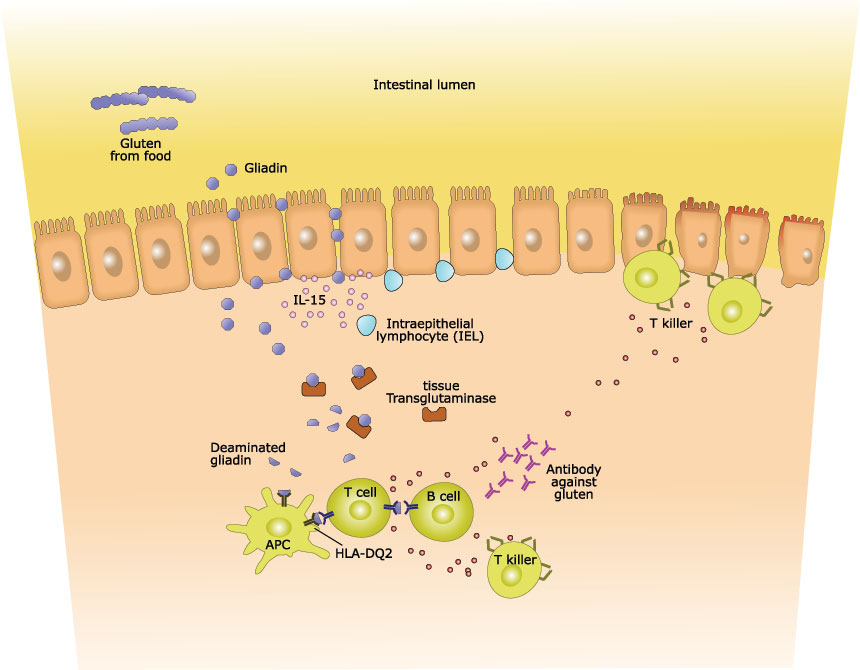
The aberrant immune response causing celiac disease is triggered by the consumption of gluten. In most cases, this immune response stops after the complete removal of dietary gluten, and the intestinal lining is gradually restored. [...]
How is Celiac Disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis of celiac disease involves medical history, physical examination and laboratory tests. The tests for celiac disease are more reliable if performed under a gluten-containing diet, as the body can only produce antibodies upon gluten [...]
What are the complications of Celiac Disease?
As the symptoms of celiac disease are often non-specific and highly variable among individuals, diagnosis of the disorder can be difficult. Complications often arise when diagnosis of celiac disease is delayed, gluten is still consumed [...]
What are the risk factors of Celiac Disease?
The etiology of celiac disease is currently unknown. However, there are risk factors that are associated with developing celiac disease. Family history People who have family history of having celiac disease or dermatitis herpetiformis have [...]
What are the signs and symptoms of Celiac Disease?
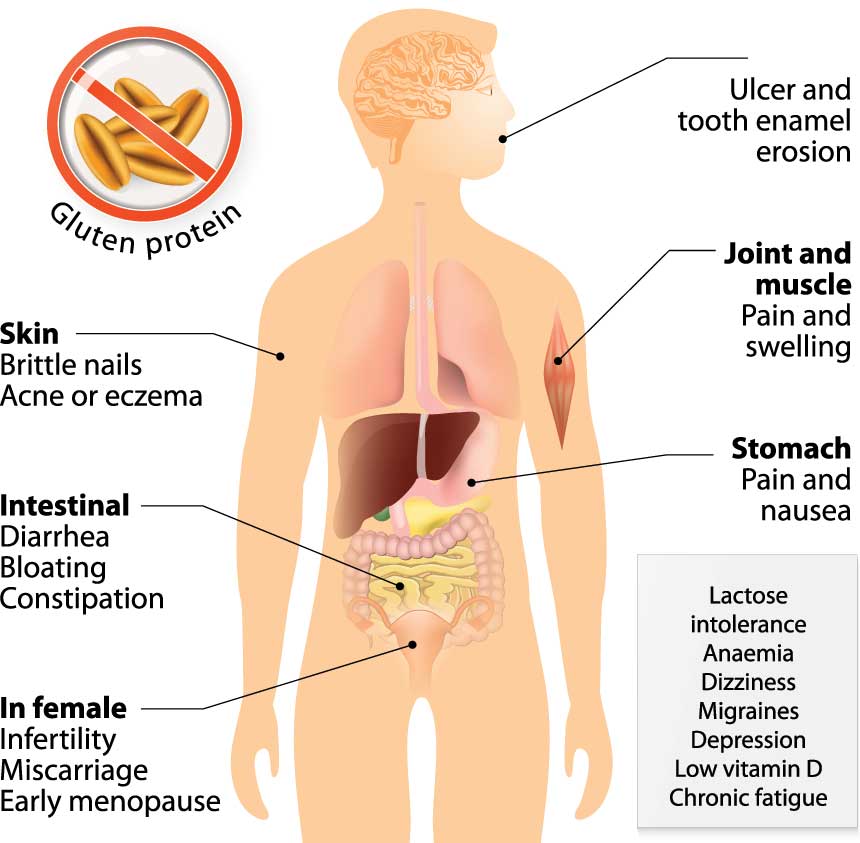
Classic celiac disease is associated with gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, weight loss, appetite changes, anorexia, lactose intolerance, abdominal distension and stools that float, appear fatty and smell foul. If the condition is left [...]
What Is Celiac Disease?
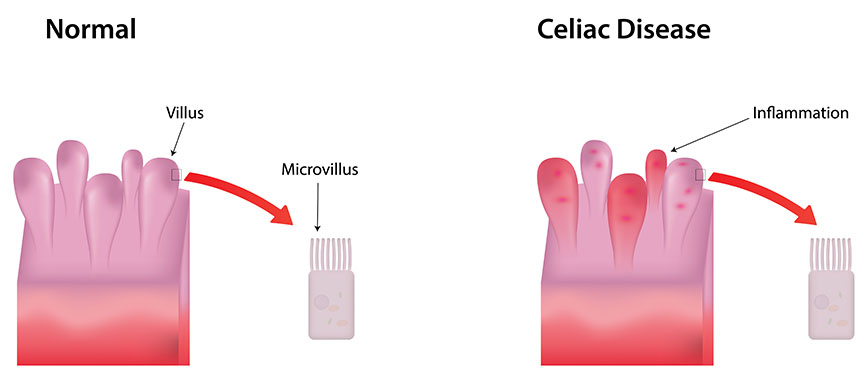
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder caused by gluten intolerance, leading to inflammation and malabsorption. In people with celiac disease, the immune system recognizes gluten as a harmful foreign substance and responds by triggering an [...]